
The Focke-Wulf Fw 190 is a German single-seat, single-engine fighter aircraft which was widely used during World War II. Along with its well-known counterpart, the Messerschmitt Bf 109, the Focke Wulf 190 became the backbone of the Luftwaffe’s Fighter Force.
The twin-row BMW 801 radial engine that powered most operational versions enabled the Fw 190 to lift larger loads than the Bf 109, allowing its use as a day fighter, fighter-bomber, ground-attack aircraft and, to a lesser degree, night fighter.
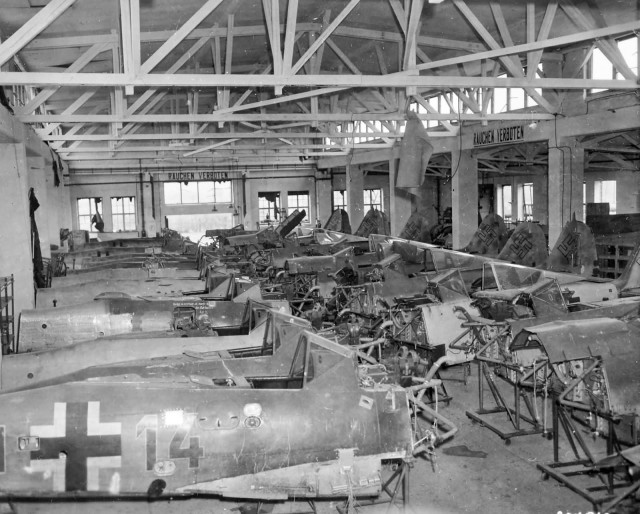 Focke-Wulf Fw 190 Fuselage Assemblies at Kolleda Germany 1945
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 Fuselage Assemblies at Kolleda Germany 1945In November/December 1942. The Fw 190 made its air combat debut on the Eastern Front, finding much success in fighter wings and specialised ground attack units called Schlachtgeschwader (Battle Wings or Strike Wings) from October 1943 onwards.
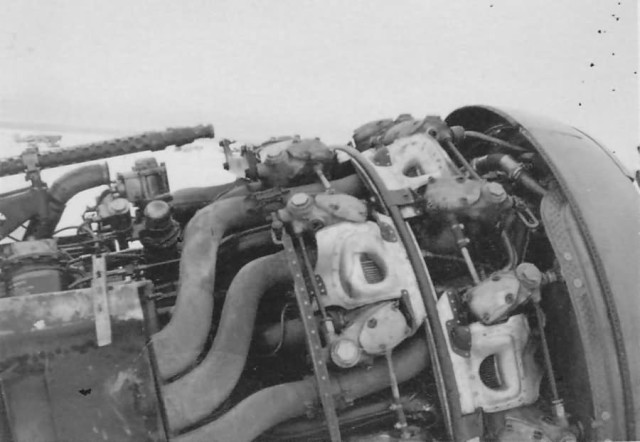 Fw 190 A of 2/JG 51 Lt. Joachim Brendel Winter 1942 1943. Engine BMW801
Fw 190 A of 2/JG 51 Lt. Joachim Brendel Winter 1942 1943. Engine BMW801The Fw 190A series’ performance decreased at high altitudes (usually20,000 ft and above), which reduced its effectiveness as a high-altitude interceptor. From the Fw 190s inception, there had been ongoing efforts to address this with a turbosupercharger BMW 801 in the B model, the C model with the Daimler-Benz DB 603, and the D model with the Junkers Jumo 213.
 Fw
190 V5k. This is the V5 with the original small wing. The 12-blade
cooling fan and redesigned undercarriage and canopy fairings are
visible.
Fw
190 V5k. This is the V5 with the original small wing. The 12-blade
cooling fan and redesigned undercarriage and canopy fairings are
visible.Problems with the turbos meant only the D model would see service, entering service in September 1944. While these “long nose” versions gave them parity with Allied opponents, it arrived far too late in the war to have any real effect.
The Fw 190 was well-liked by its pilots. Some of the Luftwaffe’s most successful fighter aces claimed a great many of their kills while flying it, including Otto Kittel, Walter Nowotny and Erich Rudorffer.
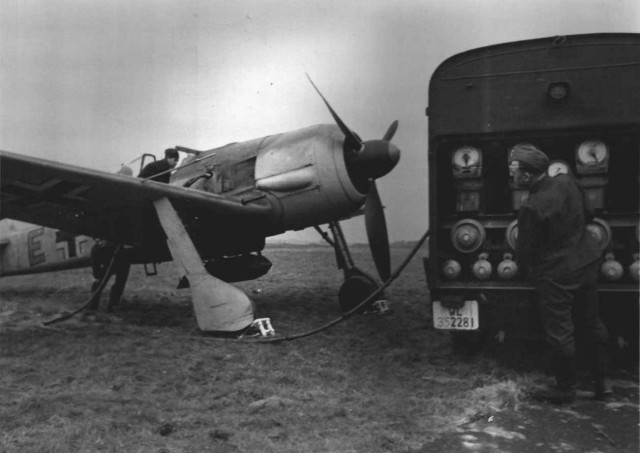 Schlachtflieger Fw 190 +E being fueled
Schlachtflieger Fw 190 +E being fueled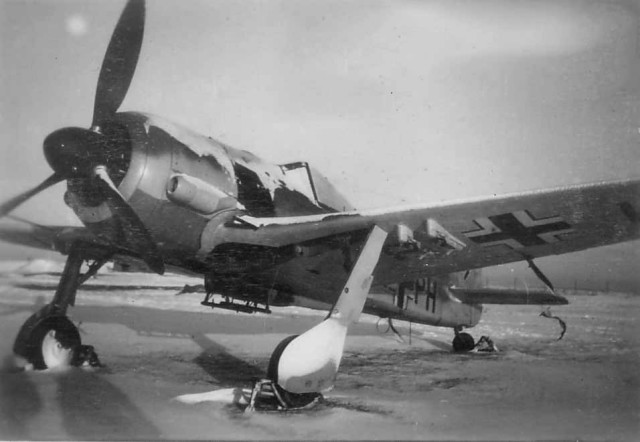 Focke-Wulf Fw 190 winter +PH
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 winter +PH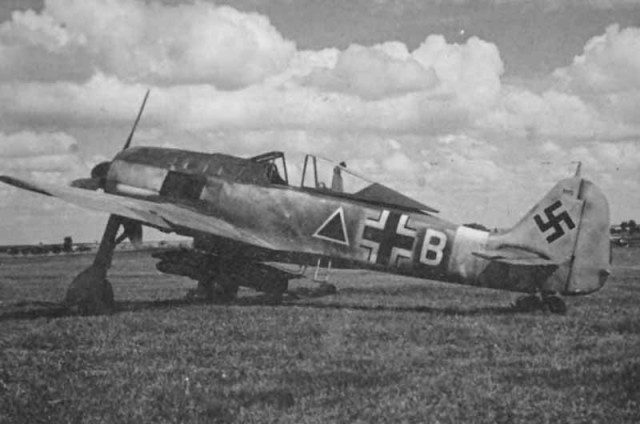 Focke-Wulf Fw 190 Jagdbomber +B
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 Jagdbomber +B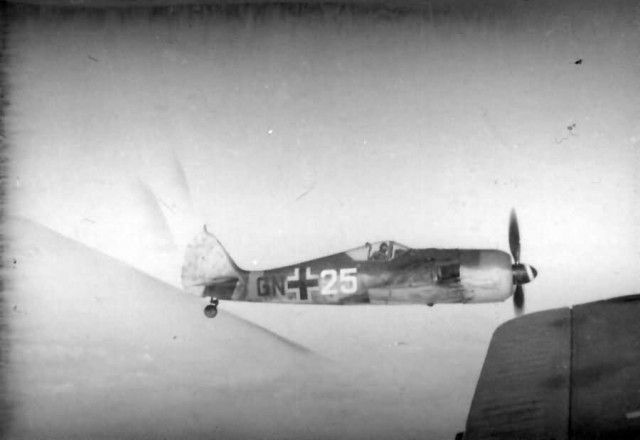 Focke-Wulf Fw 190 GN+25 in flight
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 GN+25 in flight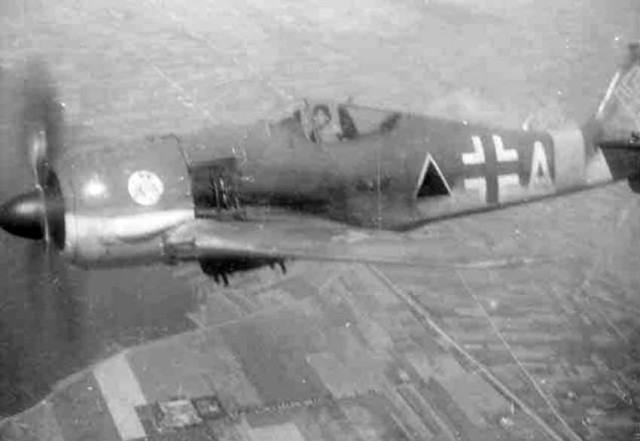 Focke-Wulf Fw 190 Jagdbomber +A
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 Jagdbomber +A Fw 190 A of 11/JG 11 Pilot Uffz. Karl Heinz 1944
Fw 190 A of 11/JG 11 Pilot Uffz. Karl Heinz 1944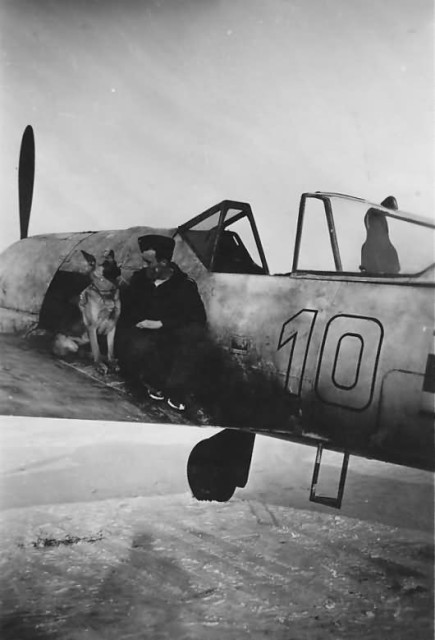 Fw 190 A white 10 of 10/JG 51 pilot Otto Gaiser, Smolensk February 1943
Fw 190 A white 10 of 10/JG 51 pilot Otto Gaiser, Smolensk February 1943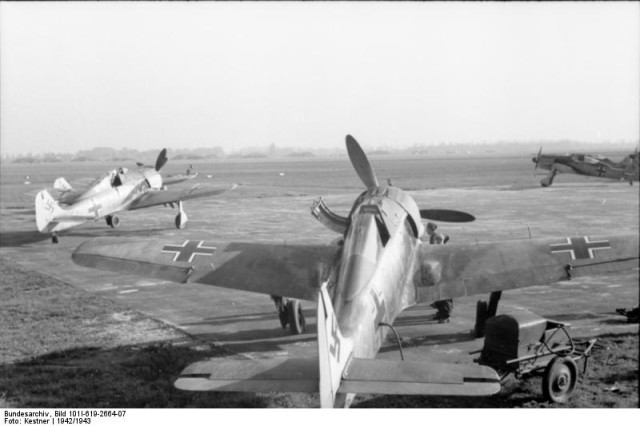 Fw 190 A-0s or A-1s of an unknown unit.
Fw 190 A-0s or A-1s of an unknown unit.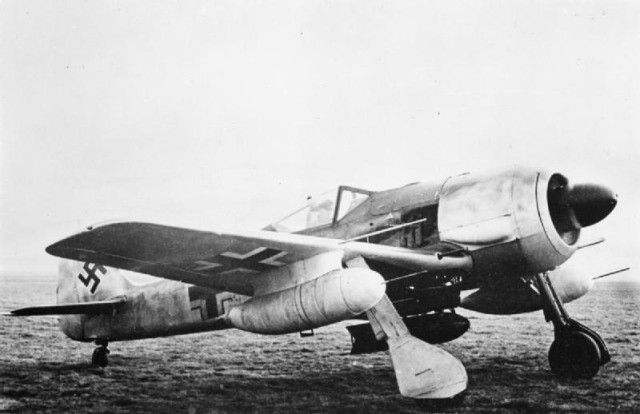 Fw 190 G-1 showing the ETC 250 bomb rack, carrying a 250 kg (550 lb) bomb, and the underwing drop tanks on VTr-Ju 87 mounts.
Fw 190 G-1 showing the ETC 250 bomb rack, carrying a 250 kg (550 lb) bomb, and the underwing drop tanks on VTr-Ju 87 mounts. A
side view of the NMUSAF’s D-9. One can easily distinguish the D-9 model
from earlier variants by the extended nose and tail sections, in
addition to the exhaust manifolds located near the base of the engine
cowling
A
side view of the NMUSAF’s D-9. One can easily distinguish the D-9 model
from earlier variants by the extended nose and tail sections, in
addition to the exhaust manifolds located near the base of the engine
cowlingWrecks / Crashes
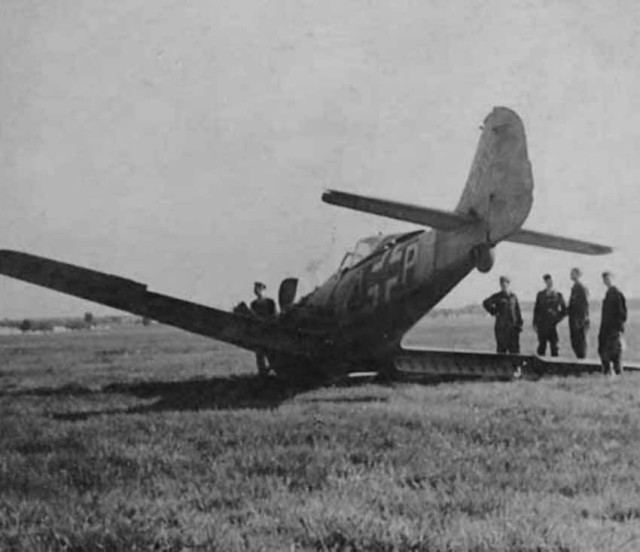 Focke-Wulf Fw 190 attack aircraft +P crash landed
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 attack aircraft +P crash landed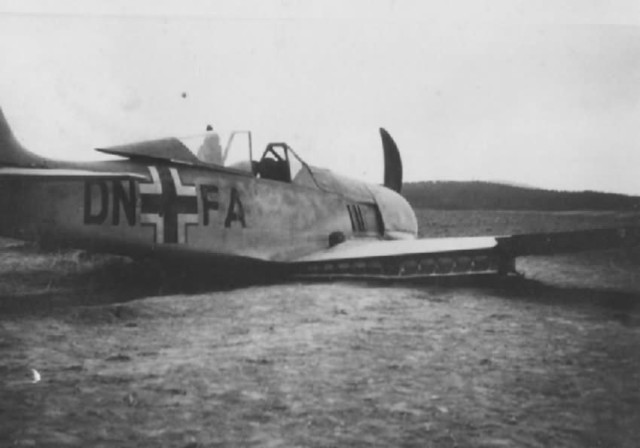 Focke-Wulf Fw 190 DN+FA crash landing
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 DN+FA crash landing Focke-Wulf Fw 190 Wreckage 2
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 Wreckage 2 Focke-Wulf Fw 190 black 10
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 black 10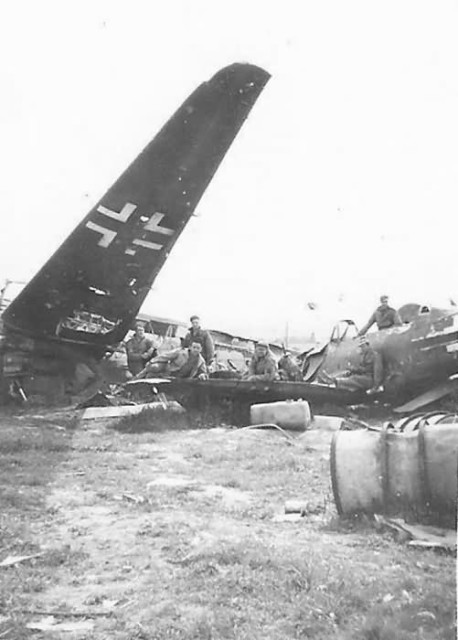 US Troops with Luftwaffe Fw 190 and Bomber Wrecks
US Troops with Luftwaffe Fw 190 and Bomber Wrecks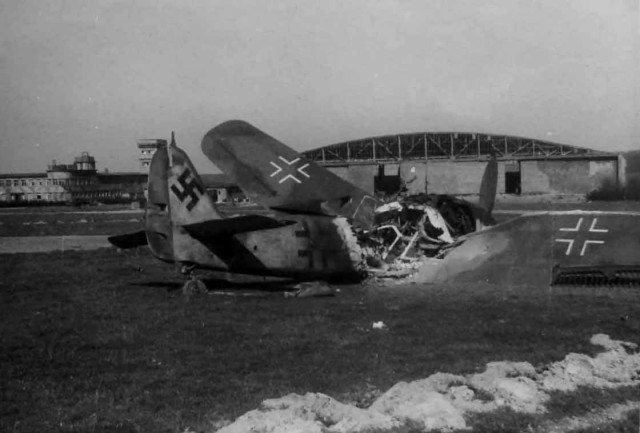 Destroyed Fw 190
Destroyed Fw 190Captured
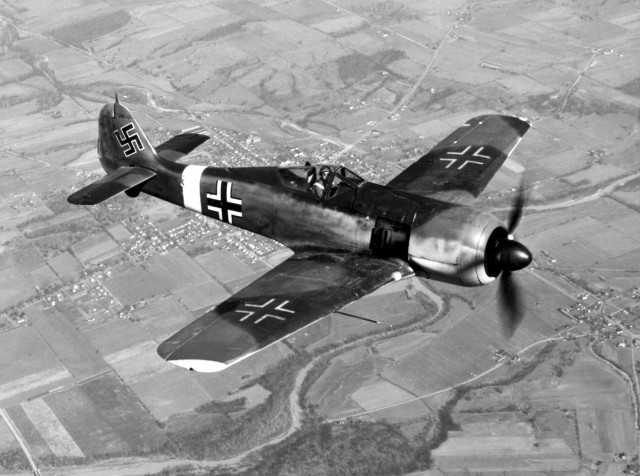 A captured Fw 190A-4. The USAAF-painted Balkenkreuz and swastika markings are of nonstandard size and proportions.
A captured Fw 190A-4. The USAAF-painted Balkenkreuz and swastika markings are of nonstandard size and proportions.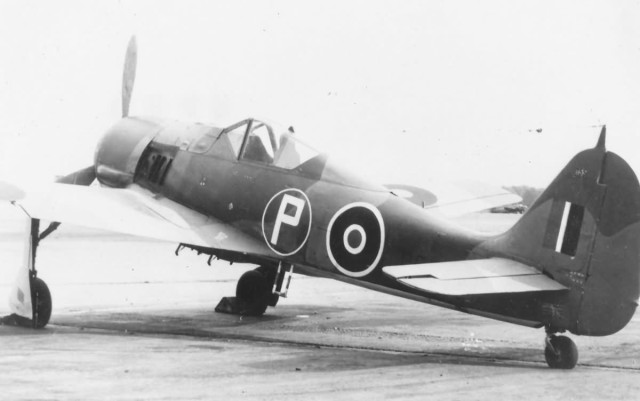 British RAF Fw 190
British RAF Fw 190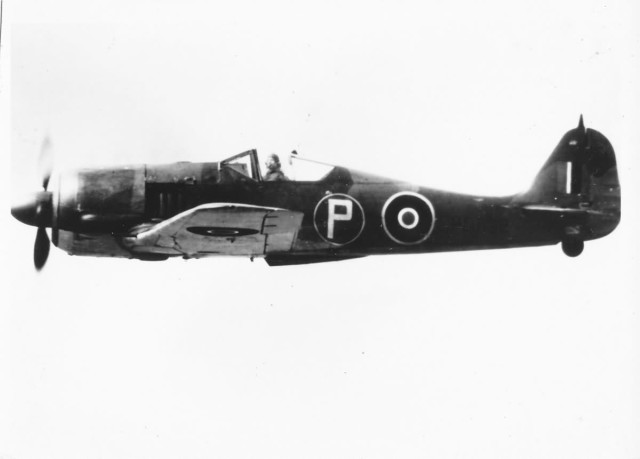 British Fw 190 in flight
British Fw 190 in flight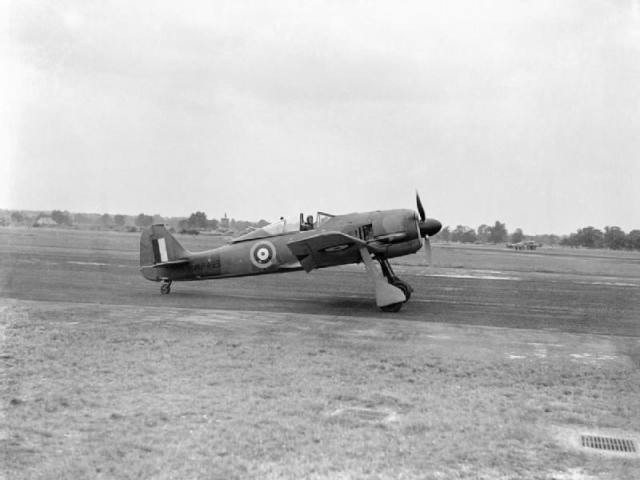 A
captured Focke-Wulf Fw 190A-3 at the Royal Aircraft Establishment
Farnborough with the RAEs chief test pilot Wing Commander H J -Willie-
Wilson at the controls August 1942.
A
captured Focke-Wulf Fw 190A-3 at the Royal Aircraft Establishment
Farnborough with the RAEs chief test pilot Wing Commander H J -Willie-
Wilson at the controls August 1942. Captured Fw 190A-5 Werknummer 150 051, in U.S. Navy colors
Captured Fw 190A-5 Werknummer 150 051, in U.S. Navy colors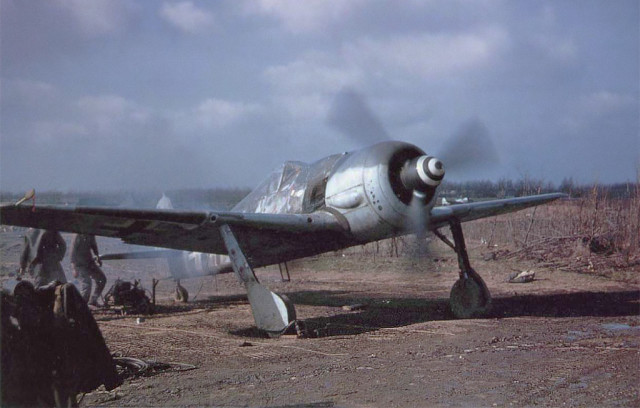 An
Fw 190 A-8/R2 in American hands. “White 11” of 5./JG 4 was captured
during Operation Bodenplatte after its engine had been damaged by
American light flak.
An
Fw 190 A-8/R2 in American hands. “White 11” of 5./JG 4 was captured
during Operation Bodenplatte after its engine had been damaged by
American light flak.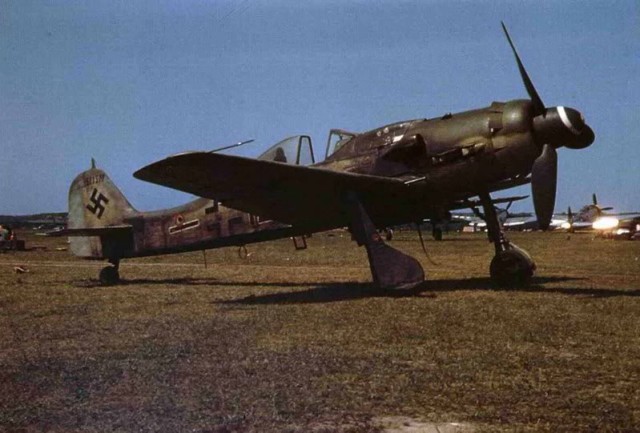 This
captured Fw 190 D-9 appears to be a late production aircraft built by
Fieseler at Kassel. It has a late style canopy; the horizontal black
stripe with white outline shows that this was a II. Gruppe aircraft.
This
captured Fw 190 D-9 appears to be a late production aircraft built by
Fieseler at Kassel. It has a late style canopy; the horizontal black
stripe with white outline shows that this was a II. Gruppe aircraft.Image sources: Wikipedia / Bundesarchiv / WorldWarPhoto

Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου